What is DHT in Hair?
One of the biggest problems with hair loss is an excess of the hormone “Dihydrotestosterone,” or DHT for short. DHT is just one of the nearly 80 hormones found in the human body. Hormones are vital for the healthy functioning of your body, but when they are imbalanced they can cause problems. In the case of DHT, there really can be too much of a good thing! If you are susceptible to its effects, it can attack your hair follicles by miniaturising them, which in turn leads to DHT hair loss in both men and women.

What is DHT?
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a male sex hormone that forms when testosterone combines with the 5-Alpha reductase enzyme. It is estimated that 10% of the testosterone produced by men and women each day is converted to DHT. Under normal conditions, women’s bodies typically have only a small amount of testosterone compared to men, but even a lower level of DHT can trigger hair loss in women.
This enzyme, 5-Alpha reductase, is held in the oil glands of hair follicles. When it combines to the testosterone it is converted to the more powerful DHT Thus, DHT can attach to the hair follicles and remain there for a long time, eventually leading to DHT hair loss.

In normal amounts, DHT is important in the following ways:
- It helps with the development of the reproductive organs, including the prostate gland.
- It establishes masculine characteristics, such as the growth of facial and body hair.
However, if the body produces too much DHT, there could be symptoms such as:
- A breakout of acne can occur.
- Because DHT drives the growth of prostate cells, excessive amounts can result in an enlarged prostate.
- Male pattern baldness is a symptom of high DHT (such as receding hairline and hair loss at the temples and on the crown).
- In women, too much DHT can result in female pattern hair loss.
- Stress can also be related to increased levels of DHT in the body.
DHT Hair Loss
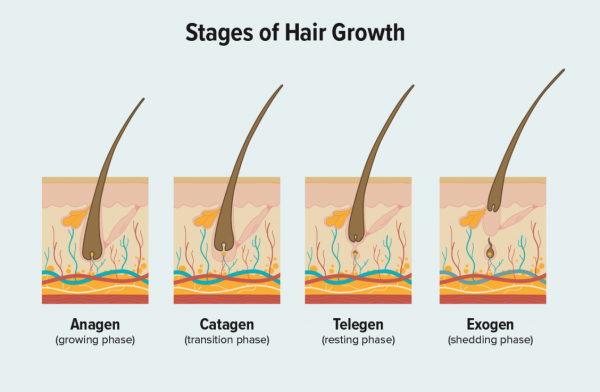
To understand how excessive DHT causes hair loss, it is necessary to look at the normal functioning of hair follicles. Each hair follicle attaches a hair into the skin and regulates the hair growth by interacting with hormones and other factors. This hair growth occurs in several stages:
Active growth phase: The length of this growth phase can vary for the different areas of hair on your body. The hairs on your head, for example, typically have a growth cycle of 2 to 5 years. During this phase, hair grows about 1 cm per month. Around 90% of your scalp hair is in this phase. This is also known as the anagen phase.
Transitional phase: This is where hair growth stops and prepares to enter the resting phase by cutting off the blood supply to the hair. This takes only a couple of weeks and, in a normal cycle, occurs in 1% of your scalp hair.
Resting phase: During this phase, the resting hair remains in the follicle until it is pushed out when a new hair begins its active growth phase. About 9% of your hair is in this resting phase, and this cycle takes about 2 to 3 months. The transitional phase and resting phase are commonly referred to as the Catagen and Telogen phases.
Shedding phase: This is when the old hair is pushed out of the pore by the new growth and becomes fully detached. Between 50 to 100 hairs are shed each day from a normal scalp. This is also know as the Exogen phase.
How does DHT affect this normal hair growth cycle?
A study conducted in 2020 by a research team of dermatologists (published in the Frontiers in Pharmacology Journal) verified the effects of different concentrations of DHT on the hair follicle, concluding that higher concentrations of DHT inhibit hair follicle growth.
DHT binds with receptors in the scalp, which eventually causes a build-up of DHT in the hair follicles. This causes miniaturisation, which shrinks the hair follicles and shortens the normal cycle of hair growth. The follicles then produce thinner hairs which are also more brittle and can fall out more easily. DHT hair loss also means it will take longer and longer for new hair to grow back. And this can eventually lead to the follicles shutting down entirely and being unable to produce hair.
How can the effects of DHT be negated?
There are two main approaches concerning how to reduce DHT:
Blocking excess production of the body’s DHT: For example, this could be achieved by something as simple as changing one’s diet towards foods that naturally block DHT production, or lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, getting regular exercise and reducing stress, etc.
Blocking DHT on the scalp: This method uses DHT blockers to prevent DHT hormones from binding directly with receptors in the scalp, thus preventing further shrinkage of the hair follicles.
Does DHT Increase With Age?
A 2002 study published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that, while testosterone levels decline with age, DHT levels seem to remain constant in men between 40 and 70 years of age. Therefore, the male pattern baldness caused by DHT will continue as the DHT hormones constantly bind with receptors in the scalp, leading to further hair follicle deterioration unless action is taken to prevent further hair loss.
Some of the DHT blockers used to address constant DHT hair loss
Pharmaceutical: Finasteride, for example, is available as a prescription medicine and reduces the effects of the enzyme that normally aids the conversion of testosterone into DHT. This means there is less DHT available to bind with the receptors in the scalp.
DHT Blocker Shampoos: These can be effective in blocking DHT’s activity on the scalp and hair follicles, plus they can wash away substances containing DHT. Some natural ingredients which act as DHT blockers are pumpkin seed oil and saw palmetto.
DHT Blocker Side Effects
With the pharmaceutical product Finasteride, common side effects are:
- Men may experience a decreased sexual desire.
- There might also be trouble having or maintaining an erection.
- It may cause ejaculation problems.
- Symptoms of an allergic reaction to Finasteride may include skin rash or swelling of the lips or face.
Unfortunately, DHT blockers will not reverse the effects of male pattern baldness. At best, they will only slow down or stop the ongoing effects of DHT hair loss. They can’t restore a receding hairline or any of the other areas of hair loss.
How can Transitions Hair help?


To restore your hair, Transitions Hair offers a variety of hair loss solutions for men and women, for every type and severity of hair loss. These include treatments such as:
Hair Loss Concealer: BioTHIK Hair Fibres are made up of microscopic natural keratin protein, the same protein that makes up your own hair. These fibres cling and seamlessly blend into your hair, hiding bald spots and receding areas instantly.
SensiGraft® is a groundbreaking hair restoration technique that bridges the gap between surgical hair transplants and typical hair replacement procedures. It is totally non-surgical yet natural-looking and undetectable, even by touch!
Laser Hair Retention Therapy has proven to be effective in promoting hair growth in males suffering from male pattern baldness. These proven procedures ensure the optimal environment for hair growth and the best results for you.
Hair Transplants utilise your own, growing hair in order to cover thinning or bald areas. Individual hair follicles are collected and relocated to other areas of your head. Not everyone is a suitable candidate for hair transplants, however, and a screening process is necessary.